SOLAR ECLIPSE 2020:
1.WHAT IS SOLAR ECLIPSE?
2.WHEN IS THE NEXT SOLAR ECLIPSE?
3.SURYAGRAHAN TIME?
4.HOW TO VIEW SOLAR ECLIPSE?
5.SOLAR ECLIPSE CHASING
6.SOLAR ECLIPSE PHOTOGRAPHY
7.OTHER IMPORTANT THING TO KNOW ABOUT SOLAR ECLIPSE
Q: WHEN IS THE NEXT SOLAR ECLIPSE :
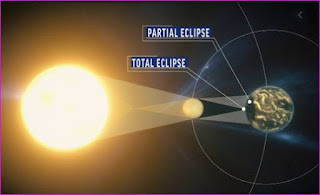
Q: What type of Eclipse will it be?
A: It will be a type of an annular or ring of fire Eclipse .
Q: Where will the next Solar Eclipse be visible?
A: It will be visible from much of Africa, Southeast Europe and most of Asia, With a partial Eclipse visible in Northern Australia
A BRIEF OF WHAT SOLAR ECLIPSE IS?
A solar eclipse occurs when a portion of the Earth is engulfed in a shadow cast by the Moon which fully or partially blocks sunlight. This occurs when the Sun, Moon and Earth are aligned. In a total eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon. In partial and annular eclipses, only part of the Sun is obscured.
 |
| SOLAR ECLIPSE |
If the Moon were in a perfectly circular orbit, a little closer to the Earth, and in the same orbital plane, there would be total solar eclipses every new moon. However, since the Moon's orbit is tilted at more than 5 degrees to the Earth's orbit around the Sun, its shadow usually misses Earth. A solar eclipse can only occur when the Moon is close enough to the ecliptic plane during a new moon. Special conditions must occur for the two events to coincide because the Moon's orbit crosses the ecliptic at its orbital nodes twice every draconic month (27.212220 days) while a new moon occurs one every synodic month (29.530587981 days). Solar (and lunar) eclipses therefore happen only during eclipse seasons resulting in at least two, and up to five, solar eclipses each year; no more than two of which can be total eclipses.
Total eclipses are rare because the timing of the new moon within the eclipse season needs to be more exact for an alignment between the observer (on Earth) and the
 |
| SOLAR ECLIPSE |
centers of the Sun and Moon. In addition, the elliptical orbit of the Moon often takes it far enough away from Earth that its apparent size is not large enough to block the Sun entirely. Total solar eclipses are rare at any particular location because totality exists only along a narrow path on the Earth's surface traced by the Moon's full shadow or umbra.
An eclipse is a natural phenomenon. However, in some ancient and modern cultures, solar eclipses were attributed to supernatural causes or regarded as bad omens. A total solar eclipse can be frightening to people who are unaware of its astronomical explanation, as the Sun seems to disappear during the day and the sky darkens in a matter of minutes.
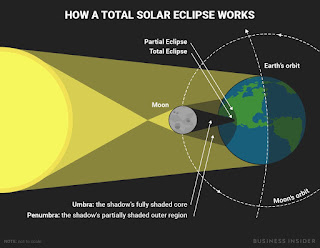 |
| HOW SOLAR ECLIPSE WORKS? |
Since looking directly at the Sun DURING SOLAR ECLIPSE can lead to permanent eye damage or blindness, special eye protection or indirect viewing techniques are used when viewing a solar eclipse. It is safe to view only the total phase of a total solar eclipse with the unaided eye and without protection. This practice must be undertaken carefully, though the extreme fading of the solar brightness by a factor of over 100 times in the last minute before totality makes it obvious when totality has begun and it is for that extreme variation and the view of the solar corona that leads people to travel to the zone of totality (the partial phases span over two hours while the total phase can only last a maximum of 7.5 minutes for any one location and is usually less). People referred to as eclipse chasers or umbraphiles will travel even to remote locations to observe or witness predicted central solar eclipses.
ON AN AVERAGE THERE ARE ABOUT 240 SOLAR ECLIPSE EACH CENTURY.
TYPES OF SOLAR ECLIPSE & THEIR OCURRENCES :
THERE ARE FOUR TYPES OF SOLAR ECLIPSE :
- TOTAL SOLAR ECLIPSE : A total eclipse occurs when the dark silhouette(A silhouette is the image of a person, animal, object or scene represented as a solid shape of a single colour) of the Moon completely obscures the intensely bright light of the Sun, allowing the much fainter solar corona to be visible.
- ANNULAR SOLAR ECLIPSE : An Annular Eclipse occurs when The Sun and Moon are exactly in line with The EARTH. But apparent size of The Moon is smaller than that of The Sun.
- HYBRID SOLAR ECLIPSE : ( It is also called as Total or Annular Eclipse ) shifts between Total and Annular eclipse.
- PARTIAL SOLAR ECLIPSE : A partial eclipse occurs when The sun and The Moon are not exactly in line with The Earth but somehow The moon obscures the sun (partially).
OCURRENCE OF TYPES OF SOLAR ECLIPSE :
- The magnitude of an eclipse is the ratio of the apparent size of The Moon to the apparent size of The Sun during an eclipse. A Total Eclipse occurs when The Moon is closest to The Earth as The Moon will completely cover The Sun's bright disk or photosphere. It has a magnitude greater than or equal to 1000.
- an eclipse that occurs when the Moon is near its farthest distance from Earth (i.e., near its apogee) can only be an annular eclipse because the Moon will appear to be slightly smaller than the Sun; the magnitude of an annular eclipse is less than 1.
- A hybrid eclipse occurs when the magnitude of an eclipse changes during the event from less to greater than one, so the eclipse appears to be total at locations nearer the midpoint, and annular at other locations nearer the beginning and end, since the sides of the Earth are slightly further away from the Moon. These eclipses are extremely narrow in their path width and relatively short in their duration at any point compared with fully total eclipses.
DURATION OF THE SOLAR ECLIPSE:
The factors that determine the duration of a total solar eclipse
- The Moon being almost exactly at perigee (making its angular diameter as large as possible).
- The Earth being very near aphelion (furthest away from the Sun in its elliptical orbit, making its angular diameter nearly as small as possible).
- The midpoint of the eclipse being very close to the Earth's equator, where the rotational velocity is greatest.
- The vector of the eclipse path at the midpoint of the eclipse aligning with the vector of the Earth's rotation (i.e. not diagonal but due east).
- The midpoint of the eclipse being near the subsolar point (the part of the Earth closest to the Sun).
The longest eclipse that has been calculated thus far is the eclipse of July 16, 2186 (with a maximum duration of 7 minutes 29 seconds over northern Guyana).
VIEWING SOLAR ECLIPSE 2020
The central path of the 2020 June annular eclipse passes through parts of African continent including Central African Republic, Congo, and Ethiopia; south of Pakistan and northern India; and China. A partial eclipse will be visible in north and east Africa, in south-east of Europe, most of Asia (except the north part of Russia) and in the north of Australia just before sunset. In Europe the partial eclipse will visible for places southeast of the line roughly passing through Perugia, Miskolc, Lviv and Yaroslavl.
- Looking directly at the photosphere of the Sun (the bright disk of the Sun itself), even for just a few seconds, can cause permanent damage to the retina of the eye, because of the intense visible and invisible radiation that the photosphere emits.
- This damage can result in impairment of vision, up to and including blindness.
- there is no warning that injury is occurring.
IMPORTANT INSTRUCTION TO VIEW SOLAR ECLIPSE 2020:
To view Annular and Partial SOLAR ECLIPSE
Viewing the Sun during partial and annular eclipses (and during total eclipses outside the brief period of totality) requires special eye protection, or indirect viewing methods if eye damage is to be avoided.
What to use : Sunglasses do not make viewing the Sun safe. Only properly designed and certified solar filters should be used for direct viewing of the Sun's disk.
What to avoid : self-made filters using common objects such as a floppy disk removed from its case, a Compact Disc, a black colour slide film, smoked glass, etc. must be avoided.
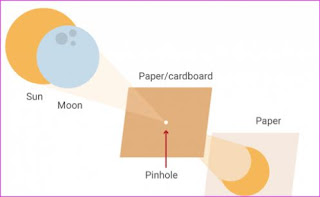
The safest way to view the Sun's disk is by indirect projection. This can be done by projecting an image of the disk onto a white piece of paper or card using a pair of binoculars (with one of the lenses covered), a telescope, or another piece of cardboard with a small hole in it (about 1 mm diameter), often called a pinhole camera. The projected image of the Sun can then be safely viewed; this technique can be used to observe sunspots, as well as eclipses.
To view Total Solar Eclipse :
When the shrinking visible part of the photosphere becomes very small, Baily's beads will occur. These are caused by the sunlight still being able to reach the Earth through lunar valleys. Totality then begins with the diamond ring effect, the last bright flash of sunlight.
It is safe to observe the total phase of a solar eclipse directly only when the Sun's photosphere is completely covered by the Moon, and not before or after totality
During this period, the Sun is too dim to be seen through filters. even solar flare may be seen.
ECLIPSE CHASING :
Eclipse Chasing generally refers to tracing the path of the sun when they occur , visible and move around the Earth.
Basically Shadow lover's chases the path of The Eclipse and they are better known as : Umbraphile.
Solar Eclipse 2020 - PHOTOGRAPHY OF SOLAR ECLIPSE
Photographing an eclipse is possible with fairly common camera equipment. In order for the disk of the Sun/Moon to be easily visible, a fairly high magnification long focus lens is needed (at least 200 mm for a 35 mm camera), and for the disk to fill most of the frame, a longer lens is needed (over 500 mm). As with viewing the Sun directly, looking at it through the optical viewfinder of a camera can produce damage to the retina, so care is recommended. Solar filters are required for digital photography even if an optical viewfinder is not used. Using a camera's live view feature or an electronic viewfinder is safe for the human eye, but the Sun's rays could potentially irreparably damage digital image sensors unless the lens is covered by a properly designed solar filter.
FINAL TOTALITY : OF SOLAR ECLIPSE
Total solar eclipses are seen on Earth because of a fortuitous combination of circumstances. Even on Earth, the diversity of eclipses familiar to people today is a temporary (on a geological time scale) phenomenon. Hundreds of millions of years in the past, the Moon was closer to the Earth and therefore apparently larger, so every solar eclipse was total or partial, and there were no annular eclipses. Due to tidal acceleration, the orbit of the Moon around the Earth becomes approximately 3.8 cm more distant each year. Millions of years in the future, the Moon will be too far away to fully occlude the Sun, and no total eclipses will occur. In the same timeframe, the Sun may become brighter, making it appear larger in size. Estimates of the time when the Moon will be unable to occlude the entire Sun when viewed from the Earth range between 650 million and 1.4 billion years in the future.
OTHER OBSERVATIONS :
GRAVITY ANOMALIES : The anomalies highlight variations in the strength of the gravitational force over the surface of the Earth.
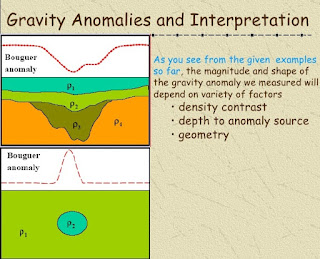 |
| GRAVITY ANOMALY |
Gravity anomalies are often due to unusual concentrations of mass in a region. For example, the presence of mountain ranges will usually cause the gravitational force to be more than it would be on a featureless planet — positive gravity anomaly. Conversely, the presence of ocean trenches or even the depression of the landmass that was caused by the presence of glaciers millennia ago can cause negative gravity anomalies.
There is a long history of observations of gravity-related phenomena during solar eclipses, especially during the period of totality.
Observation during the 1997 solar eclipse by Wang et al. suggested a possible gravitational shielding effect, which generated debate. In 2002, Wang and a collaborator published detailed data analysis, which suggested that the phenomenon still remains unexplained
ARTIFICIAL SATELLITE ECLIPSE :
New possibilities have been opened up by recent developments in the field of astronautics, enabling us to inject in different orbits artificial satellites of the Earth. In principle there are two distinct categories of satellites operating in the eclipse domain:
Passive satellites in the form of huge balloons reflecting the solar radiation towards the Earth's surface where photometrical measurements can be performed if the geometrical and meteorological conditions are favourable.
Active satellites furnished with photometrical equipment and telemetering their indications to the terrestrial tracking stations.
Over the lunar eclipses we have many advantages accompanied, however, by some minor disadvantages. Among the former we can count: Very great frequency of satellite eclipses - several tens per year -in comparison with 2 - 3 possible eclipses in the same time interval.
 |
| ARTIFICIAL ECLIPSE |
Great selectivity in the altitude, the light beam having in the upper atmosphere a vertical extension smaller than for lunar eclipses
Great selectivity in latitude, as the effective part of the shadow terminator is very small « 100 km)
Artificial satellites can also pass in front of the Sun as seen from the Earth, but none is large enough to cause an eclipse. At the altitude of the International Space Station, for example, an object would need to be about 3.35 km (2.08 mi) across to blot the Sun out entirely. These transits are difficult to watch because the zone of visibility is very small.
Possibility to explore the short wave radiations with active satellites.
Nevertheless, some disadvantages or difficulties of satellite eclipses should be mentioned in all objectivity:
- Necessity of an exact ephemeris. This problem was solved a long time ago for the Moon but remains outstanding especially for balloon satellites whose motion is capricious.
- Irregular shape of the balloon satellites in combination with their rotation sometimes deforms the light curve during the eclipse.
- Necessity of tracking the satellite. This operation is more complicated than for the slow-moving Moon.
- Irregularities or perturbations affecting the complicated apparatus of active satellites.
THESE OBSERVATIONS ARE NOT SUBJECT TO WEATHER CONDITIONS.
EARTHSHINE DURING SOLAR ECLIPSE : During a total solar eclipse, the Moon's shadow covers only a small fraction of the Earth. The Earth continues to receive at least 92 percent of the amount
of sunlight it receives without an eclipse – more if the penumbra of the Moon's shadow partly misses the Earth. Seen from the Moon, the Earth during a total solar eclipse is mostly brilliantly illuminated, with only a small dark patch showing the Moon's shadow. The brilliantly-lit Earth reflects a lot of light to the Moon.
 |
| EARTHSHINE |
THE MOON DURING TOTAL SOLAR ECLIPSE APPEARS TO BE BLACK
SOLAR ECLIPSE SEASON :
Generally a Solar Eclipse occurs two weeks after or before of a Lunar Eclipse. Mostly there are two eclipses seen in a row, however, there could as many as three eclipses in a season. The June-July season of eclipses will witness three eclipse. On June we witnessed a Penumbral Lunar Eclipse. On June 21 we are about to witness an Annular Solar Eclipse. On July 5, there will again be a Penumbral Lunar Eclipse taking place.
ECLIPSE IN ANCIENT HISTORY :
As best as we can determine, the earliest record of a solar eclipse occurred over four millennia ago. In China, it was believed that the gradual blotting out of the sun was caused by a dragon who was attempting to devour the sun, and it was the duty of the court astronomers to shoot arrows, beat drums and raise whatever cacophony they could to frighten the dragon away.
In the ancient Chinese classic Shujing (or Book of Documents) is the account of Hsi and Ho, two court astronomers who were caught completely unaware by a solar eclipse, having gotten drunk just before the event began. In the aftermath, Zhong Kang, the fourth emperor of the Xia dynasty ordered that Hsi and Ho be punished by having their heads chopped off. The eclipse in question was that of Oct. 22 in the year 2134 B.C.
In the Bible, in the book of Amos 8:9, are the words, “I will cause the sun to go down at noon, and I will darken the Earth in the clear day.” Biblical scholars believe this is a reference to a celebrated eclipse observed at Nineveh in ancient Assyria on June 15, 763 B.C. An Assyrian tablet also attests to the event.
A solar eclipse even stopped a war.
According to the historian Herodotus, there was a five-year war that raged between the Lydians and the Medes. As the war was about to move into its sixth year, a Greek sage, Thales of Miletus foretold to the Ionians that the time was soon approaching when day would turn to night. On May 17, 603 B.C. the sun faded away just as Thales had alluded that it would. So believing that it was a sign from above, the combatants called a truce, which was cemented by a double marriage, for, as Herodotus wrote: “Without some strong bond, there is little of security to be found in men’s covenants.”
Advertisement
And giving new meaning to the term, “Scared to death,” is the timid emperor Louis of Bavaria, the son of Charlemagne, who witnessed an unusually long total eclipse of the sun on May 5, A.D. 840, which lasted for over five minutes. But no sooner had the sun begun to emerge back into view, Louis was so overwhelmed by what he had just seen that he died of fright!
solar eclipse
SOURCE OF THIS : SPACE.COM
total solar eclipse
eclipse 2017
solar eclipse 2017
ANNULAR solar eclipse 2020, total eclipse,
total eclipse 2020,
sun eclipse,
when is the next solar eclipse,
solar eclipse today,
solar eclipse 2020 map,
2020 eclipse map,
solar eclipse glasses,
june 21 2020,
lunar eclipse 2020,
sun eclipse 2020,
solar eclipse calendar,
partial solar eclipse,
eclipses 2020,
august 2020 eclipse,
next total solar eclipse,
solar and lunar eclipse,
total solar eclipse 2020 map,
partial eclipse,
solar eclipse 2020 best location,
GUYS GET READY WITH A CARDBOARD WITH A HOLE IN IT'S CENTER THIS 21st JUNE TO LOOK AT AN AMAZING ANNULAR ECLIPSE .
COMMENT DOWN FOR OTHER UPDATES AND FOLLOW US TO GET UPDATE OF OUR LATEST POST.
source : wikipedia
THANKS & REGARDS
THE DYNHACKS TEAM











No comments:
Post a Comment