Why Are Job Boards Failing Job Seekers? The Jobs Platform Fixes It.
The Problem No One Wants to Talk About
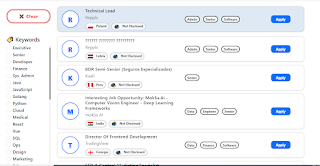 |
| The Jobs Platform |
It’s a problem that plagues every major job board out there: LinkedIn, Naukri, RemoteOK, Wellfound. They claim to have thousands of jobs, but for job seekers, it's like wading through a swamp of disappointment. You click on job after job, only to realize you’re not actually qualified. You waste time. You get demotivated. And let’s be real—after the 50th rejection, you start questioning your entire career.
Why Do Job Boards Do This?
Most job platforms don’t actually care about experience matching. They focus on bulk listings, not personalization. Even the ones that claim to filter jobs by experience take the lazy way out. They create ‘bins’ like 0-3 years experience, which is a wide gap. If you're a fresher, seeing roles requiring even two years of experience makes you feel like you don’t belong.
The result? You either apply to jobs you have no chance at, or you give up entirely. Neither is good.
The Jobs Platform: A Smarter Way to Job Hunt
Enter The Jobs Platform (https://thejobsplatform.com), a first-of-its-kind job board that actually does what every other platform pretends to do. It lets you filter jobs based on your actual experience level—no nonsense, no guesswork.
 |
| Personalized Dashboard |
Here’s how it works:
Experience-Based Job Matching – Unlike traditional job boards, The Jobs Platform ensures that you only see jobs that match your exact experience level. If you have 0 years of experience, you’ll only see jobs that require 0 years—no hidden ‘2-3 years’ surprises. If you have 1 year of experience, you’ll see jobs requiring up to 1 year—ensuring you're only applying to roles you're actually qualified for.
Global & Remote Jobs – Unlike traditional job boards that focus on a single region, The Jobs Platform aggregates jobs from all over the world. Whether you’re looking for remote, hybrid, or country-specific roles, they’re all here in one place.
Verified Listings – Fake job postings? Not here. Unlike some platforms that let anyone post anything, The Jobs Platform ensures that every job is legitimate.
Why This Matters
Imagine the difference this makes. Instead of spending hours filtering through irrelevant jobs, you log in, see openings that match your actual qualifications, and apply with confidence. It’s job searching without the emotional rollercoaster.
For job seekers at all levels, this is a game-changer. No more false hope. No more time wasted. Just real opportunities that actually fit.
The Future of Job Hunting
The job search process is broken, and most platforms aren’t fixing it. They make money from job postings, not from actually helping job seekers. But The Jobs Platform is different. It puts you first, ensuring that your time isn’t wasted on mismatched roles.
If you’re tired of being gaslit by traditional job boards, it’s time to switch to a platform that actually works for you.
